When it comes to laundry room installations, understanding the correct washer box height is crucial for both functionality and compliance with building codes. This often-overlooked aspect of plumbing can make the difference between a smoothly operating laundry system and one plagued with drainage issues, water hammer, or code violations. Whether you’re a homeowner planning a renovation, a contractor working on new construction, or a DIY enthusiast tackling a laundry room project, getting the washer box height right from the start will save you time, money, and frustration down the line.
What Is a Washer Box and Why Does Height Matter?
A washer box, also known as a washing machine outlet box or laundry box, is a recessed fixture installed in the wall behind your washing machine. This essential plumbing component houses the hot and cold water supply valves and the drain connection for your washing machine. The box keeps these connections organized, protected, and easily accessible while maintaining a clean, finished appearance in your laundry room. Unlike exposed pipes that can be damaged or create an unsightly tangle of hoses, a properly installed washer box provides a professional solution that integrates seamlessly with your wall.
The height at which you install your washer box directly impacts several critical factors in your laundry system’s performance. Proper washer box height ensures adequate drainage through gravity, prevents siphoning and backflow issues, allows for proper venting of the drain system, and provides convenient access for connecting and disconnecting hoses. When installed at the incorrect height, you may experience slow drainage, gurgling sounds from the drain, water backing up into the machine, difficulty reaching connections, and potential code violations that could affect home inspections or insurance claims.
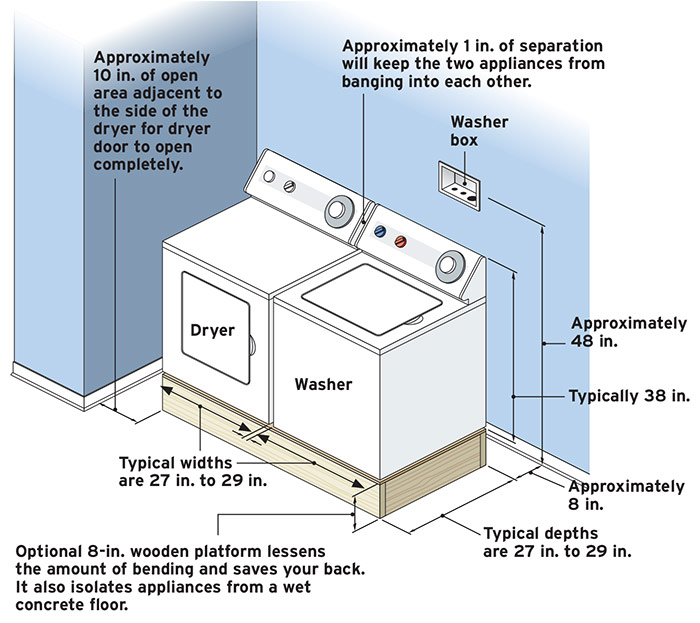
According to plumbing standards and building codes, the standard washer box height typically ranges from 42 to 48 inches from the finished floor to the center of the outlet box. This range has been established through decades of plumbing practice and represents the optimal balance between drainage efficiency and user accessibility. However, understanding why this specific range exists requires a deeper look at the mechanics of washing machine drainage and the principles of drain-waste-vent (DWV) systems.
Suggested read: Reducing Washer: Everything You Need to Know About This Essential Plumbing Component
Standard Washer Box Height Requirements and Building Codes
The height of washer boxes isn’t arbitrary—it’s carefully calculated based on plumbing principles and codified in the International Plumbing Code (IPC) and Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC). These codes provide the framework that local jurisdictions use to establish their specific requirements, though some municipalities may have additional regulations or slight variations. Understanding these standards is essential for any installation, whether you’re doing the work yourself or hiring a professional.
Minimum and Maximum Height Standards
The International Plumbing Code specifies that the standpipe for a washing machine drain must extend at least 18 inches above the trap weir, with the trap weir typically located near floor level. This creates a minimum effective height that prevents the washing machine’s discharge pump from creating a siphon effect that could drain the trap seal. When you factor in the trap location and the need for proper drainage, this translates to a washer box mounting height that typically falls between 42 and 48 inches measured from the finished floor to the centerline of the box.
Key Height Specifications:
- Minimum standpipe height: 18 inches above trap weir
- Maximum standpipe height: 96 inches (8 feet) above trap weir
- Recommended washer box center height: 42-48 inches from finished floor
- Optimal height for front-load washers: 42-44 inches
- Optimal height for top-load washers: 44-48 inches
- Commercial applications: May require 48-54 inches depending on equipment
The maximum height restriction of 96 inches exists to ensure that the washing machine’s pump can effectively discharge water without excessive back pressure. Modern washing machines typically have pumps capable of lifting water 8 feet vertically, but installing the drain connection at this maximum height leaves no margin for error and can strain the pump, potentially shortening its lifespan.
Regional Code Variations
While the IPC and UPC provide national standards, individual states, counties, and municipalities may have their own interpretations or additional requirements for washer box height specifications. For example, California has historically followed the UPC more closely, while many eastern states adhere to the IPC. Some jurisdictions require specific venting configurations that may influence the optimal box placement, while others have requirements about the box depth or the spacing between water valves.
Before beginning any installation, always check with your local building department to obtain the specific requirements for your area. Many municipalities now offer online access to their adopted building codes, making it easier to research requirements before starting your project. Professional plumbers working in your area will be familiar with local code variations and can ensure compliance during installation.
Suggested read: Pan Washer: Everything You Need to Know About This Essential Plumbing Component
Determining the Right Washer Box Height for Your Situation
Selecting the optimal washer box height for your specific installation involves more than just following the code minimums. Several factors unique to your situation should influence your final placement decision, ensuring that your laundry system operates efficiently while remaining convenient to use for years to come.
Type of Washing Machine Considerations
Front-loading and top-loading washing machines have different ergonomic considerations that affect the ideal washer box height. Front-load washers, which have become increasingly popular due to their energy efficiency and larger capacities, typically sit lower to the ground and have their connection points at the back of the machine. For these units, a washer outlet box height of 42 to 44 inches works well because it positions the connections at a comfortable height relative to the top of the machine, making it easier to reach behind the unit without excessive bending or stretching.
Top-load washers generally sit slightly higher and may have their connection area positioned differently depending on the model. For these machines, a height of 44 to 48 inches often provides better accessibility. If you’re installing a laundry pedestal or platform under your washing machine—a common choice for front-loaders to reduce bending when loading and unloading—you’ll need to add the pedestal height (typically 12 to 16 inches) to your calculations. In this case, a washer box mounted at the standard 42-inch height might end up too low relative to the raised machine, so you may want to consider placing it at 48 inches or even slightly higher, always staying within code requirements.
User Height and Accessibility Requirements
The physical characteristics of the primary laundry room users should factor into your washer box placement decision. A household with taller individuals might find a box mounted at 48 inches more comfortable to work with, reducing the need to bend when connecting or disconnecting hoses. Conversely, if primary users are shorter or if accessibility is a concern, positioning the box at 42 inches may provide better reach without requiring a step stool.
For households with mobility challenges or wheelchair users, specific ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) guidelines may apply, particularly in multi-family housing or if you’re seeking universal design certification for your home. While ADA doesn’t specify exact washer box heights, the principle of accessible reach ranges (typically 15 to 48 inches from the floor for forward reach) should guide your installation. In these cases, consulting with an accessibility specialist can help you optimize the placement for your specific needs while maintaining code compliance.
Stackable Units and Compact Spaces
Stackable washer-dryer combinations present unique challenges for washer box height determination. When units are stacked vertically, the washing machine is typically on the bottom, and its drain connection height needs to account for the unit’s specific configuration. Many stackable units have connection points on the side or back that may be higher than traditional washers. Measure your specific unit’s connection locations before finalizing the box height, and consider that you’ll need to access these connections from either the side or by pulling the entire stack forward—a task that’s more difficult with stacked units than with standalone machines.
Suggested read: ONR Wash: The Waterless Car Cleaning Revolution That's Changing Vehicle Care Forever
Installation Process and Best Practices for Optimal Washer Box Height
Installing a washer box at the correct height requires careful planning, precise measurements, and attention to plumbing fundamentals. Whether you’re roughing in a new construction project or retrofitting an existing laundry room, following proper installation procedures ensures your washer box height meets code requirements while providing reliable, long-term performance.
Pre-Installation Planning and Measurements
Before cutting into any walls or purchasing materials, create a detailed plan for your laundry room layout. Start by determining the exact location where your washing machine will sit, accounting for the machine’s dimensions, door swing clearance, and any adjacent cabinetry or appliances. Measure from the finished floor—not the subfloor—to ensure your washer box mounting height is accurate once flooring materials are installed. If you haven’t installed flooring yet, add the thickness of your chosen flooring material to your calculations. Ceramic tile, for instance, can add 3/8 to 1/2 inch, while luxury vinyl plank might add 1/4 inch.
Mark the centerline of your washer box location on the wall, typically centered behind where the washing machine will sit. Most washing machines are 27 to 29 inches wide, so centering the box behind this space provides the best access. Verify that your chosen location doesn’t conflict with wall studs, electrical circuits, or other utilities in the wall cavity. Use a stud finder to locate framing members, and consider using an endoscopic camera or borescope if you need to verify what’s inside the wall before cutting.
Rough-In Requirements and Plumbing Connections
The rough-in plumbing work must be completed before installing the washer box itself. Your drain line, typically 2-inch PVC or ABS pipe, should run horizontally through the wall cavity to the washer box location with proper slope for drainage—generally 1/4 inch of fall per foot of horizontal run. The trap for the washing machine drain should be installed according to code, usually with a P-trap located within the wall cavity or immediately below the washer box location. This trap must maintain a water seal to prevent sewer gases from entering your home while being positioned to prevent siphoning during the washer’s discharge cycle.
Critical Rough-In Components:
- Drain line: 2-inch minimum diameter
- Drain slope: 1/4 inch per foot minimum
- Trap location: As close to washer box as practical
- Hot water supply: 1/2-inch copper, PEX, or CPVC
- Cold water supply: 1/2-inch copper, PEX, or CPVC
- Supply line shutoff valves: Quarter-turn ball valves recommended
- Water hammer arrestors: Often required by code, always recommended
- Vent connection: Must comply with local venting requirements
The hot and cold water supply lines should be brought to the washer box location with proper support and protection against freezing if the laundry room is in an exterior wall or unconditioned space. Install shutoff valves that will mount inside the washer box, positioning them at the appropriate height so they’ll be easily accessible when the box is installed. Quarter-turn ball valves are preferred over traditional compression valves because they’re easier to operate, less prone to leaking, and provide positive shutoff.
Installing the Washer Box at the Correct Height
With rough-in plumbing complete and inspected, you can install the washer box itself. Most modern washer boxes are designed to fit between standard 16-inch on-center wall studs and come in various depths to accommodate different wall thicknesses. Measure from your finished floor to the 42 to 48-inch mark (or your chosen height within this range) and mark the centerline of where the box will sit. The box should be level and securely fastened to the wall studs using appropriate fasteners—typically screws through the box’s mounting flanges.
Position the box so that its front edge will be flush with the finished wall surface once drywall or other wall covering is installed. If you’re installing the box before drywall, you’ll need to account for the drywall thickness (typically 1/2 inch or 5/8 inch) by setting the box back from the stud faces accordingly. Many washer boxes have adjustable mounting flanges or depth markers to help you achieve the correct positioning. Once secured, connect your supply valves to the rough-in plumbing, ensuring all connections are tight and leak-free. Connect the drain outlet on the box to your drain pipe, using appropriate fittings and ensuring proper slope is maintained.
Suggested read: Commercial Glass Washers: Why Your Business Needs Professional Glassware Cleaning Equipment
Common Problems Related to Incorrect Washer Box Height
Installing a washer box at the wrong height can lead to various operational problems, some of which may not become apparent until you’ve been using your washing machine for weeks or months. Understanding these potential issues helps illustrate why proper washer box height is so critical and what problems you might encounter if your existing installation isn’t optimal.
Drainage and Siphoning Issues
The most common problem associated with incorrect washer drain height is poor drainage or siphoning. When a washer box is installed too low—below the recommended 42-inch minimum—the standpipe may not provide sufficient height above the trap to prevent siphoning. During the washing machine’s spin cycle, it pumps water out forcefully, and if the drain connection is too low, this forceful discharge can create enough suction to pull water out of the trap. Once the trap seal is broken, sewer gases can enter your home, creating unpleasant odors and potentially exposing your household to harmful gases like methane and hydrogen sulfide.
Conversely, if the washer box is mounted too high—approaching or exceeding the 96-inch maximum specified in plumbing codes—your washing machine’s pump may struggle to lift water to that height. This can result in slow drainage, water backing up into the machine during the spin cycle, error codes on modern computerized washers, increased wear on the pump mechanism, and potential flooding if water can’t drain quickly enough. These problems are particularly noticeable with older washing machines that have less powerful pumps or when the drain line has additional restrictions like multiple bends or partial clogs.
Access and Maintenance Challenges
A washer box installed at an improper height can make routine maintenance and emergency repairs unnecessarily difficult. If mounted too high, you may need a step stool or ladder to reach the shutoff valves—inconvenient during normal operation and potentially dangerous during an emergency when you need to quickly shut off water to a leaking hose. A box positioned too low requires excessive bending or kneeling to access connections, which can be particularly problematic for individuals with mobility issues or back problems.
The ideal washer box height should allow an average-height person to comfortably reach all connections while standing naturally, without stretching on tiptoes or bending at an uncomfortable angle. When you need to disconnect hoses for cleaning the inlet screens (recommended annually), move the washing machine for maintenance, or respond to a leak, accessible connections at the proper height make these tasks much simpler and safer.
Code Violations and Inspection Failures
Perhaps the most serious consequence of incorrect washer box height installation is failing to meet building code requirements. During home construction, additions, or major renovations requiring permits, plumbing inspections will verify that washer boxes are installed within code-specified heights. An installation that doesn’t meet these requirements will fail inspection, requiring costly corrections before you can proceed. Even if your work doesn’t require a permit, code violations can create problems when selling your home, as home inspectors may flag non-compliant installations in their reports, potentially affecting your sale price or requiring repairs as a condition of sale.
Insurance implications can also arise from non-code-compliant plumbing installations. If a washing machine overflow or leak causes water damage and an insurance adjuster determines that improper installation contributed to the problem, your claim could be denied or reduced. While it’s rare for insurance companies to investigate the specific height of washer boxes, egregious violations combined with resulting damage could raise questions about the overall quality of your home’s plumbing system.
Suggested read: Embassy Wash: The Ultimate Solution for Professional Glass Cleaning and Detailing
Measuring and Adjusting Existing Washer Box Height
If you’ve moved into a home with an existing laundry room or you’re experiencing problems that might be related to washer box height, measuring and potentially adjusting the existing installation may be necessary. While relocating a washer box is more involved than installing one correctly the first time, it’s often possible to make adjustments that improve functionality and bring the installation into compliance with current codes.
How to Measure Your Current Washer Box Height
To determine your existing washer box height, you’ll need a tape measure and access to the area behind your washing machine. Pull the machine forward enough to see the washer box clearly—you may need a helper to move the machine safely without damaging flooring or disconnecting hoses. Measure from the finished floor surface directly to the center of the washer box, which is typically where the drain connection enters the box. Take note of this measurement and compare it to the standard range of 42 to 48 inches.
While you have access to the area, inspect the overall condition of your washer box installation. Look for signs of leaking around water supply connections, corrosion on valves or fittings, cracks in the box itself, or improper drain connections. Check that water hammer arrestors are installed (they look like short vertical pipes capped on top, usually 6 to 12 inches tall, located on the hot and cold supply lines). These devices protect your plumbing system from pressure spikes when the washing machine’s solenoid valves shut off suddenly, and while not always required by older codes, they’re highly recommended for modern high-efficiency washers that can create significant water hammer.
Options for Adjusting Washer Box Height
If your measurements reveal that your washer outlet box is outside the recommended height range, you have several options depending on the severity of the problem and your budget. For minor height discrepancies—say, a box installed at 40 inches when 42 inches would be better—you might choose to live with the installation if it’s functioning properly and not causing drainage issues. However, if you’re experiencing problems or planning a laundry room renovation, adjustment or relocation might be worthwhile.
Relocation Options:
- Complete relocation: Remove the existing box and rough-in plumbing, reroute water supply and drain lines, and install a new box at the correct height. This is the most comprehensive solution but also the most expensive and disruptive, typically requiring drywall removal, patching, and repainting.
- Vertical adjustment: If the box is only slightly too low or high and your plumbing configuration allows it, you may be able to adjust the drain connection and water supply lines vertically without completely relocating the box. This requires cutting into the wall and may involve extending or rerouting pipes.
- Standpipe extension: For boxes that are too low but have drainage issues, extending the standpipe height above the trap can sometimes resolve siphoning problems without moving the entire box. This addresses the functional problem without the cosmetic benefit of a properly positioned box.
- Retrofit solutions: Some manufacturers make adjustable washer boxes designed for retrofit situations, with flexible mounting options that can work with existing rough-in locations while providing a more finished appearance.
Any significant plumbing modifications should be performed by a licensed plumber or, if you’re doing the work yourself, should be properly permitted and inspected according to local requirements. Remember that plumbing work often affects your home’s resale value and insurability, so professional installation with proper documentation provides peace of mind and protects your investment.
Suggested read: Dr Wash: Transform Your Vehicle Care with Professional Auto Detailing Services
Washer Box Height for Special Situations and Applications
Not all laundry installations follow standard residential patterns. Understanding how washer box height requirements vary in special situations helps ensure proper installation regardless of your specific circumstances. From commercial laundromats to multi-family housing to unique residential configurations, each scenario may have different optimal heights and code requirements.
Multi-Story Buildings and High-Rise Applications
In apartment buildings, condominiums, and other multi-story residential structures, washer box installation height must account for additional factors beyond typical single-family considerations. Drain stacks in multi-story buildings serve multiple units, and the timing of discharge from various washing machines can create pressure fluctuations in the drain system. Proper venting becomes even more critical, and the height of the washer box relative to the main building drain and vent stack affects system performance.
Building codes for multi-family housing often have additional requirements for washing machine connections, including mandatory water hammer arrestors, specific trap configurations, and requirements for individual shut-off valves accessible from outside the unit for emergency situations. The washer box height in these applications typically follows the same 42 to 48-inch range as single-family homes, but the supporting infrastructure must be more robust to handle the demands of multiple units potentially running wash cycles simultaneously.
Commercial and Laundromat Installations
Commercial laundry facilities have unique requirements that affect washer drain box height decisions. Commercial washing machines are typically larger and more powerful than residential units, with pumps capable of higher discharge rates and vertical lift. Some commercial units discharge water at rates exceeding 50 gallons per minute, compared to 15 to 20 gallons per minute for residential machines. This higher flow rate requires larger drain lines—typically 3 inches instead of 2 inches—and may necessitate different height considerations to ensure proper drainage.
Commercial installations often position washer boxes higher than residential standards, sometimes in the 48 to 54-inch range, to accommodate the larger machines and provide easier access for maintenance staff who work with these connections frequently. Commercial plumbing codes may differ from residential codes, and facilities must comply with additional regulations regarding commercial fixture units, trap sizing, and venting. Always consult with a commercial plumber familiar with laundromat installations when planning these facilities, as the consequences of improper installation can be much more severe in a commercial context where downtime directly impacts revenue.
Outdoor and Garage Laundry Installations
Installing laundry facilities in garages, outdoor laundry rooms, or unconditioned spaces introduces challenges related to freezing protection, weatherproofing, and code compliance. The washer box height in these applications follows the same general standards, but additional considerations include protecting water supply lines from freezing, using weather-resistant washer box materials if exposed to outdoor conditions, ensuring proper venting that doesn’t allow sewer gases to accumulate in enclosed garage spaces, and providing adequate drainage that accounts for floor slope and potential freezing conditions.
In regions with cold winters, any water supply line in an unconditioned space must be protected against freezing, either through insulation, heat tape, or by keeping the space heated. Even if pipes are protected, having them in an exposed garage wall installed at the standard 42 to 48-inch height makes them more vulnerable than pipes running through interior walls. Consider using a slightly lower installation height (while staying within code) to keep supply lines lower in the wall where heat from the home’s interior might provide some protection, or ensure that the entire wall cavity around the washer box is extremely well insulated.
Suggested read: The Complete Camper Wash Blueprint: Transform Your RV From Filthy to Sparkling in 2025
Washer Box Height and Modern High-Efficiency Washing Machines
The evolution of washing machine technology has implications for optimal washer box height that weren’t considerations when older codes were written. Modern high-efficiency (HE) washers operate differently from traditional agitator-style machines, with different water usage patterns, spin speeds, and drainage characteristics that can affect the ideal height for washer boxes serving these appliances.
High-Efficiency Washer Drainage Characteristics
High-efficiency front-load washers typically spin at much higher RPMs than traditional top-loaders—often 1,200 to 1,400 RPM compared to 600 to 900 RPM for older machines. These higher spin speeds mean water is expelled more forcefully during the drain cycle, creating more potential for siphoning if the washer drain box height is inadequate. The positive side of this forceful discharge is that HE washers can typically pump water to the full 96-inch maximum standpipe height without difficulty, giving you more flexibility in placement if your situation requires a higher installation.
However, HE washers also use less water overall—often 15 to 20 gallons per load compared to 30 to 40 gallons for traditional washers. This lower water volume means that drain cycles are shorter but more intense, and the reduced water flow can sometimes be more affected by restrictions in the drain line than the higher-volume flow of traditional machines. Ensuring that your washer box height provides adequate venting and proper trap seal becomes even more important with these machines, as the forceful, concentrated discharge can create significant pressure changes in the drain system.
Smart Washers and Error Codes Related to Drainage
Modern smart washing machines equipped with sensors and computerized controls can detect drainage problems and display error codes when they occur. Common error codes related to improper washer box height or drainage issues include “dE” or “drain error” codes indicating that water isn’t draining quickly enough, “OE” or “overflow error” codes suggesting water is backing up into the machine, “Sud” codes that can sometimes be triggered by drainage restrictions causing excessive suds due to water backing up, and pressure sensor errors that may indicate drain line restrictions or siphoning issues.
If your HE washing machine regularly displays these error codes, checking your washer box installation height and the overall condition of your drain system should be among your first troubleshooting steps. Sometimes these errors aren’t caused by the washer box height itself but by restrictions in the drain line, improper venting, or clogs that developed over time. However, an incorrectly positioned washer box can exacerbate these problems or make them more likely to occur.
Water Hammer and Pressure Surge Protection
Modern washing machines with electronic solenoid valves can create significant water hammer—pressure surges that occur when water flow is suddenly stopped. These pressure surges can damage plumbing connections, cause pipes to vibrate and make noise, and potentially lead to leaks over time. While water hammer arrestors aren’t always required by code for washing machine installations, they’re increasingly considered best practice, especially with HE washers that use fast-acting electronic valves.
When installing a washer box at the proper height, incorporating water hammer arrestors into the installation provides valuable protection for your plumbing system. These devices—essentially sealed chambers with an air cushion that absorbs pressure spikes—should be installed on both the hot and cold water supply lines, typically within the washer box itself or immediately adjacent to it. Some modern washer boxes come with built-in water hammer arrestor chambers, making installation simpler while providing necessary protection.
Suggested read: Best Boat Wash Solutions: How to Keep Your Vessel Spotless in 2025
Tools and Materials Needed for Proper Washer Box Height Installation
Successfully installing a washer box at the correct height requires having the right tools and materials on hand before beginning work. While the specific items you need may vary depending on your exact installation situation, the following list covers the essentials for most washer box height installation projects.
Essential Tools for Installation
Measurement and Layout Tools:
- Tape measure (25-foot minimum recommended)
- Level (2-foot or 4-foot recommended)
- Stud finder
- Pencil or marker for marking cut lines
- Square for ensuring accurate angles
Cutting and Demolition Tools:
- Drywall saw or reciprocating saw for wall opening
- Hacksaw or PVC saw for cutting drain pipes
- Utility knife for drywall and material scoring
- Drill with various bits for pilot holes and mounting screws
Plumbing Tools:
- Pipe wrench or adjustable wrench for supply connections
- Channel locks or pliers for various fittings
- PVC primer and cement for drain connections (if using PVC)
- Teflon tape or pipe thread sealant for threaded connections
- Tubing cutter for copper or PEX supply lines (if applicable)
Installation and Finishing Tools:
- Screwdriver set for mounting hardware
- Caulk gun for sealing around box perimeter
- Trowel or putty knife for drywall patching
- Sandpaper for finishing drywall repairs
Required Materials and Components
The materials you’ll need for a complete washer box installation at proper height include the washer box itself, appropriate supply valves, drain components, and finishing materials. When selecting a washer box, choose one rated for your wall depth—typically 2×4 construction (3.5-inch wall depth) or 2×6 construction (5.5-inch wall depth). Boxes are available in various configurations, including single-piece molded polymer boxes (most common), metal boxes with separate components, boxes with integrated water hammer arrestors, and boxes with or without built-in drain connections.
Required Materials List:
- Washer outlet box appropriate for wall depth
- Quarter-turn ball valves (hot and cold)
- Water hammer arrestors (if not integrated in box)
- 2-inch PVC or ABS drain pipe and fittings
- P-trap assembly (if not already in place)
- 1/2-inch supply line pipe (copper, PEX, or CPVC)
- Appropriate fittings for supply connections
- Mounting screws (usually provided with box)
- Drywall (if cutting new opening)
- Joint compound and tape for drywall finishing
- Paintable caulk for sealing around box
- Paint matching wall color for finishing
When purchasing your washer box, verify that it meets local code requirements and is appropriate for your specific installation. Some jurisdictions require specific types of boxes or have preferences for certain materials. Boxes are relatively inexpensive—typically $30 to $80 for residential units—but choosing quality components with good warranties can prevent future problems and ensure long-term reliability.
Suggested read: Wash Depot: Your Ultimate Destination for Professional Vehicle Cleaning Solutions
Professional Installation vs. DIY for Washer Box Height Projects
Deciding whether to tackle washer box height installation yourself or hire a professional plumber depends on several factors, including your skill level, the complexity of your specific situation, and local code requirements regarding permits and inspections. Understanding what’s involved in professional installation versus DIY approaches helps you make an informed decision that balances cost considerations with quality and safety concerns.
When to Hire a Professional Plumber
Certain situations strongly favor hiring a licensed plumber for washer box installation rather than attempting the work yourself. If you’re dealing with any of the following circumstances, professional installation is likely your best choice: major plumbing system modifications requiring permits and inspections, installations in multi-family housing where code requirements are more stringent, situations requiring complex drain rerouting or venting modifications, installations in walls containing other utilities where mistakes could be costly, any work involving main drain lines or building drain stacks, and installations in areas where mistakes could cause significant water damage to finished spaces below.
Professional plumbers bring several advantages beyond just technical skill. They’re familiar with local code requirements and can ensure your installation will pass inspection on the first try. They carry insurance that protects you from liability if something goes wrong during installation, and they typically warranty their work, providing recourse if problems develop. The cost of professional installation for a washer box typically ranges from $300 to $800, depending on your location, the complexity of the installation, and whether rough-in plumbing is already in place. While this may seem expensive compared to DIY costs, it’s relatively modest compared to the potential cost of fixing mistakes or dealing with water damage from improper installation.
DIY Installation Considerations
If you have basic plumbing skills and experience with home renovation projects, installing a washer box at the proper height can be a manageable DIY project, particularly if you’re working in new construction or a major renovation where walls are already open. Successful DIY installation requires carefully researching local code requirements, obtaining any necessary permits before beginning work, taking accurate measurements and double-checking them before cutting, working methodically and not rushing through critical steps, knowing when to call a professional if you encounter unexpected problems, and having your work inspected if required by local code.
The DIY cost for materials typically ranges from $100 to $250, depending on the specific components you choose and whether you need to purchase specialized tools you don’t already own. Remember that this doesn’t include the cost of permits (typically $50 to $150 if required) or any expenses related to mistakes or problems encountered during installation. One common pitfall for DIYers is underestimating the time required—what might seem like a four-hour project can easily stretch to a full weekend when you encounter unexpected challenges like hidden obstacles in the wall cavity, supply lines that need rerouting, or drain connections that don’t align as planned.
If you do choose to tackle the project yourself, work carefully and don’t hesitate to consult with or call in a professional if you encounter anything beyond your skill level. Plumbing mistakes can be expensive to repair, and the modest savings from DIY installation aren’t worth the risk if you’re not confident in your abilities. Many plumbers are willing to consult on DIY projects, reviewing your plans and offering guidance even if you’re doing the actual installation work yourself—a middle-ground approach that can provide valuable expertise while still allowing you to save on labor costs.
Suggested read: Wash Assist: Transform Your Laundry Experience with Smart Technology
Washer Box Height and Related Components: Complete System Integration
Understanding washer box height is just one part of creating a properly functioning laundry room plumbing system. The washer box integrates with several other components, each of which must be correctly sized, positioned, and installed for optimal performance. Looking at the complete system helps you appreciate how all these elements work together and why proper planning is so important.
Water Supply System Components
The water supply system that feeds your washing machine begins at your home’s main water line and includes several components before reaching the washer box. Your main shutoff valve controls water to the entire house and should be accessible in case of emergencies. From there, branch lines run to various fixtures throughout your home, including the hot and cold lines that supply your laundry room. These lines should be adequately sized—1/2-inch minimum for residential washers—and properly supported throughout their run.
At the washer box location, the supply lines terminate at shutoff valves installed within the box itself. Using quality washer lock washer assemblies and proper threaded connections ensures these critical joints remain leak-free. The valves should be easy to operate, even after years of service, which is why quarter-turn ball valves are preferred over traditional compression valves that can become difficult to turn or develop leaks over time. From these shutoff valves, flexible washing machine hoses (typically supplied with the washing machine) connect to the back of the machine itself, completing the supply path.
Drain System and Venting Requirements
The drain system removes wastewater from your washing machine and conveys it to your home’s main drain line or septic system. This system must be properly sized, sloped, and vented to function correctly. The drain begins at the washer box, where the washing machine’s discharge hose inserts into the standpipe. This standpipe must extend to the proper height above the trap to prevent siphoning—typically 18 inches minimum, which is one reason the washer box height standards exist.
Below the washer box, a P-trap creates a water seal that prevents sewer gases from entering your home. This trap must remain filled with water at all times, and proper washer drain height helps ensure that the washing machine’s discharge doesn’t create enough suction to siphon water out of the trap. From the trap, the drain line slopes downward at the required 1/4-inch per foot minimum, conveying wastewater to the main drain line. This horizontal run should be as short and direct as possible, with minimal bends that could restrict flow or collect debris.
Venting is critical for proper drain function. Every plumbing trap requires a vent that allows air into the drain system, preventing negative pressure that could siphon water from traps or slow drainage. The specific venting requirements for washing machine drains vary by code and situation, but typically involve either a dedicated vent pipe running upward through the roof or connection to an existing vent stack within a specified distance from the trap. Some installations use air admittance valves (AAVs) as an alternative to traditional venting, though not all jurisdictions permit these devices. Improper venting is one of the most common causes of drainage problems even when the
Integration with Laundry Room Design
The washer box height and location significantly impact your overall laundry room layout and design. When planning a new laundry room or renovating an existing one, consider the box placement in relation to other elements like cabinetry, countertops, utility sinks, and storage solutions. A washer box centered behind the washing machine at 42 to 48 inches works well in most layouts, but you may need to adjust placement if you’re incorporating custom cabinetry or specialized storage solutions.
If your laundry room design includes upper cabinets or shelving above the washing machine area, ensure that the washer box height doesn’t conflict with these elements. You’ll need clearance to pull the washing machine forward for maintenance and to access the connections within the box. Many designers recommend leaving at least 6 inches of clear space above the washing machine for this purpose, though more is better if your ceiling height allows. This clearance becomes particularly important if you’re using a washer lock washer system or other specialized connection hardware that may extend above the standard hose connections.
Counter-height installations have become popular in modern laundry room designs, where the washing machine and dryer are raised on a platform with storage drawers underneath, and a continuous countertop spans across both appliances. In these configurations, the washer outlet box height must account for the platform height while still maintaining proper drainage clearances. A typical counter-height platform adds 12 to 15 inches to the floor height, which would suggest mounting the washer box at 54 to 60 inches from the actual floor—but remember that code requirements are measured from the finished floor, not from the platform surface. In most cases, you’d still mount the box at the standard 42 to 48-inch range, and it would simply be lower relative to the raised appliances, which actually makes connections easier to access when you pull the appliances forward.
Suggested read: Unimac Washer: Everything You Need to Know Before Buying
Maintaining Your Washer Box Installation Over Time
Once your washer box is installed at the proper height, ongoing maintenance ensures continued reliable performance and helps prevent problems before they become serious. Regular attention to your washing machine connections and drain system can extend the life of both your appliances and your plumbing infrastructure while avoiding water damage and costly repairs.
Routine Inspection and Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance for your washer box area should include these important tasks performed at the recommended intervals:
Quarterly checks:
- Inspect washing machine hoses for bulges, cracks, or signs of deterioration
- Verify that connections at both the washer box and machine are tight and leak-free
- Check the area around the washer box for signs of moisture or water damage
- Ensure shutoff valves operate smoothly and completely close water flow
Annual maintenance:
- Replace washing machine supply hoses (every 3-5 years at minimum, annually if using rubber hoses)
- Clean inlet screen filters on washing machine and supply valves
- Test water hammer arrestors by listening for banging pipes when washer valves close
- Inspect drain hose for kinks, restrictions, or buildup
- Pour drain cleaner or enzymatic treatment into standpipe to prevent clogs
As-needed tasks:
- Address any leaks immediately, even small drips that seem insignificant
- Replace corroded or difficult-to-operate shutoff valves before they fail
- Clear any lint or debris buildup around drain connections
- Verify proper washer box height if you replace your washing machine with a different model
The washing machine supply hoses deserve special attention in your maintenance routine. These hoses operate under constant water pressure and are subject to stress every time the washing machine fills and drains. Standard rubber hoses have a recommended lifespan of only 3 to 5 years, while stainless steel braided hoses can last longer but should still be inspected regularly. Failed supply hoses are one of the most common causes of household water damage, with insurance industry data showing these failures cause hundreds of millions of dollars in damage annually. Replacing hoses on a preventive schedule is far less expensive than dealing with water damage from a burst hose.
Recognizing Warning Signs of Problems
Understanding the warning signs of problems related to your washer box installation helps you address issues before they become serious. Common indicators that your washer box or drain system needs attention include:
- Slow drainage: Water backing up into the washing machine during drain cycles suggests restrictions in the drain line or inadequate venting
- Gurgling sounds: Air bubbles or gurgling from the standpipe indicate venting problems or partial clogs
- Sewer odors: Smells around the laundry area suggest the trap seal has been lost, possibly due to siphoning from incorrect washer drain height
- Water spots or stains: Discoloration on walls near the washer box indicates leaks that may be intermittent or hidden
- Mold or mildew: Growth around the washer box area signals ongoing moisture problems from leaks or condensation
- Difficult valve operation: Shutoff valves that are hard to turn are at risk of failure when you need them most
- Washing machine error codes: Frequent drainage errors on your machine may indicate plumbing system problems rather than appliance issues
If you notice any of these warning signs, investigate and address the root cause promptly. Many problems start small but escalate quickly once they begin. A minor leak that drips occasionally may not seem urgent, but over time it can cause significant damage to wall materials, promote mold growth, and potentially damage flooring or ceilings in rooms below your laundry area. Similarly, drainage problems that start as occasional slow draining can progress to complete blockages that require emergency plumbing service and may result in wastewater overflow.
Dealing with Mineral Buildup and Hard Water
In areas with hard water—water containing high levels of dissolved minerals like calcium and magnesium—mineral buildup can affect washing machine supply lines, valves, and connections over time. This buildup reduces water flow, can cause valves to stick or leak, and may restrict the opening where hoses connect to supply valves. If you live in a hard water area, incorporating specific maintenance tasks related to mineral management helps protect your washer box installation.
Installing a water softener or conditioning system provides the most comprehensive solution to hard water problems, benefiting not just your laundry connections but your entire plumbing system. If a whole-house system isn’t practical, point-of-use water treatment specifically for your washing machine can help. Periodically cleaning supply valve screens and washing machine inlet filters with vinegar helps dissolve mineral deposits before they cause restriction problems. If shutoff valves become difficult to operate due to mineral buildup, replacing them with new valves is often more practical than attempting to clean severely affected valves.
The washer box height can actually affect how mineral problems manifest. Mineral-rich water sitting in supply lines at higher elevations may show more pronounced buildup due to pressure and temperature variations, while proper drainage at the correct height helps prevent standing water in the drain system where minerals could precipitate and create clogs. Maintaining proper water flow throughout your system, enabled by correct installation height and functioning components, provides the best defense against mineral-related problems.
Suggested read: Sultan Wash: The Ultimate Solution for Commercial Laundry Excellence
Energy Efficiency and Water Conservation Considerations
While washer box height might not seem directly related to energy efficiency or water conservation, the overall design of your laundry plumbing system—including proper box placement—can impact these important considerations. Modern approaches to sustainable building and resource conservation have implications for how we think about laundry room plumbing.
Efficient Drainage and Reduced Pump Strain
A properly positioned washer box at the correct height allows your washing machine to drain efficiently with minimal pump strain. When the drain connection is positioned within the optimal 42 to 48-inch range, your washing machine’s pump operates within its designed parameters, using only the energy necessary to lift and expel water the intended distance. If the washer drain box height is excessive, forcing the pump to work against greater vertical lift, your machine uses more electricity to pump water out during each drain cycle.
Over the lifespan of a washing machine—typically 10 to 15 years with hundreds or thousands of wash cycles—even small efficiency losses add up to significant energy waste. Additionally, pumps working under excessive strain experience more wear and are more likely to fail prematurely, necessitating repairs or machine replacement sooner than would otherwise be needed. From both an energy conservation and appliance longevity perspective, optimal washer box placement contributes to sustainable operation.
Gray Water Systems and Alternative Drainage
Some environmentally conscious homeowners incorporate gray water systems that capture and reuse water from washing machines for irrigation or other non-potable purposes. These systems require specialized plumbing configurations that may affect washer box height requirements. Gray water systems typically involve diverting washing machine discharge to a filtering and storage system rather than directly to the sewer or septic system.
When incorporating gray water capture into your laundry plumbing design, work with professionals experienced in these systems to ensure proper integration. The washer box height may need adjustment to accommodate gravity-fed gray water routing or to provide proper clearance for filtering equipment. Additionally, gray water systems must comply with local regulations, which vary significantly by jurisdiction—some areas actively encourage these systems with streamlined permitting, while others prohibit them entirely or impose strict requirements that make them impractical for residential use.
Modern low-flow washing machines optimized for water conservation work best with properly configured drainage systems that can handle the concentrated discharge these machines produce. Ensuring your washer outlet box is positioned correctly supports efficient operation of these water-saving appliances, contributing to overall resource conservation goals while maintaining excellent cleaning performance.
Suggested read: Dexter Washer For Commercial Laundry Owners: What You Need To Know
Comparing Washer Box Options and Features
Not all washer boxes are created equal, and the specific box you choose for your installation can affect both initial installation ease and long-term performance. Understanding the features available in different washer box designs helps you select the best option for your specific washer box height installation requirements.
Standard Washer Box Designs
Single-piece molded polymer boxes represent the most common option for residential installations. These units typically feature an integrated design with mounting flanges, valve connection points, and drain inlet molded as one piece. Advantages include affordable pricing (typically $30-$60), lightweight construction that simplifies installation, corrosion-resistant materials that won’t deteriorate over time, and availability at most home improvement stores. The main limitation is that these boxes come in fixed depths for specific wall thicknesses, so you must choose the correct model for your 2×4 or 2×6 wall construction.
Metal washer boxes constructed from galvanized steel or other metals offer increased durability but come with trade-offs. These boxes can support heavier loads if you plan to mount anything on the box itself, and they resist impact damage better than polymer units. However, metal boxes cost more ($60-$100+), may corrode over time especially in humid environments, and are heavier, making installation slightly more challenging. Metal boxes are more common in commercial applications where durability and heavy-use considerations outweigh cost concerns.
Recessed box-and-trim combinations provide a more finished appearance with a decorative trim plate that covers the wall opening around the rough-in box. These systems offer a cleaner aesthetic and often include features like color-matched trim plates or brushed metal finishes. The trade-off is higher cost ($80-$150) and slightly more complex installation. For high-end residential projects or visible laundry areas where appearance matters, these premium options may be worth the additional investment.
Special Features and Add-Ons
Several advanced features available in modern washer boxes address specific needs or provide enhanced performance beyond basic models:
Integrated water hammer arrestors built into the box design eliminate the need to install separate arrestor devices on your supply lines. These boxes typically cost $70-$120 but simplify installation while ensuring proper water hammer protection. The integrated arrestors are sized appropriately for washing machine applications and positioned optimally relative to the shutoff valves.
Drain flow enhancers in some premium boxes include features like smooth internal drain transitions, enlarged drain connections, or built-in vent accommodations that improve drainage performance. These features can be particularly valuable in installations where the washer box height is near the minimum or maximum allowed ranges, helping ensure reliable drainage even under less-than-ideal conditions.
Adjustable depth boxes use sliding or telescoping components to accommodate varying wall depths, providing flexibility if you’re unsure of exact wall thickness or working with non-standard construction. These boxes typically cost $50-$90 and can save you from ordering the wrong box or needing to make modifications during installation.
Frost-proof designs for installations in unheated spaces include features like insulated compartments or drain valve configurations that allow water to drain completely from the box when not in use. These specialized boxes are essential for garage or outdoor installations in freezing climates and typically cost $100-$200.
When selecting your washer box, balance your budget against the specific requirements of your installation. For straightforward residential installations at standard washer box heights in conditioned spaces, a quality basic polymer box from a reputable manufacturer will serve you well for decades. For more demanding applications or situations where enhanced features would provide meaningful benefits, investing in premium options can prove worthwhile.
Suggested read: Crosley Washer: Everything You Need to Know Before Your Next Laundry Appliance Purchase
Regional and International Variations in Washer Box Standards
While this article has primarily focused on standards common in the United States, it’s worth noting that washer box height requirements and laundry plumbing practices vary internationally. Understanding these variations is important if you’re working on projects in different countries or regions, or if you’re consulting information sources from different areas.
North American Standards
In the United States and Canada, the International Plumbing Code (IPC) and Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC) provide the foundation for most local plumbing regulations, with the 42 to 48-inch washer box height range representing standard practice. However, Canadian provinces may have additional requirements or variations, and Mexico follows different plumbing standards that can affect installation practices. Throughout North America, the trend has been toward standardization, making it easier for plumbers and contractors working across jurisdictions to maintain consistent practices.
The washer drain height standards in North America evolved from practical experience and have been refined over decades of residential plumbing practice. The current standards represent a consensus that balances drainage effectiveness, user accessibility, pump capabilities of typical washing machines, and construction practicalities. While specific numerical values may vary slightly between jurisdictions, the fundamental principles remain consistent across the continent.
European and International Approaches
European plumbing standards approach washing machine installations somewhat differently than North American practice. Many European homes use combination washer-dryer units or compact washing machines that may have different connection requirements than full-size North American washers. The washer box height concepts still apply, but the specific implementations may vary significantly.
In many European countries, washing machines often connect to existing plumbing rather than dedicated washer boxes, with supply connections at standard fixture heights and drain connections that may use different configurations than the standpipe approach common in North America. Additionally, European washing machines often have different electrical requirements (220-240V compared to North American 110-120V) which affects appliance performance and capabilities.
Asian, Australian, and other international markets each have their own standards and practices for laundry plumbing. If you’re working on international projects or consulting international sources for information about washer box installation, be aware that measurements, standard practices, and code requirements may differ significantly from North American norms. Always verify local requirements and work with professionals familiar with local practices when working outside your familiar jurisdiction.
Suggested read: Washed Stone: Everything You Need to Know About Clean Aggregate for Your Next Project
Frequently Asked Questions About Washer Box Height
What is the standard height for a washer box?
The standard washer box height ranges from 42 to 48 inches measured from the finished floor to the center of the outlet box. This range has been established through plumbing codes and best practices to ensure proper drainage while providing convenient access to connections. Within this range, 42-44 inches works well for front-load washers, while 44-48 inches is often optimal for top-load machines.
Can a washer box be installed at 36 inches?
Installing a washer box at 36 inches is below the recommended standard and may violate local plumbing codes. At this height, the standpipe may not provide sufficient height above the trap to prevent siphoning issues, which can lead to drainage problems and loss of the trap seal. If you have an existing installation at 36 inches experiencing problems, consult with a licensed plumber about adjusting the height or implementing solutions to improve drainage performance.
How high should a washing machine drain be from the floor?
The washing machine drain standpipe should extend at least 18 inches above the trap weir, with the trap typically located near floor level. When you factor in the trap location and the need for the standpipe to extend above it, this translates to a washer box mounting height of 42-48 inches from the finished floor for optimal performance and code compliance.
Does washer box height affect drainage?
Yes, washer box height significantly affects drainage performance. A box installed too low may result in siphoning problems where water is pulled from the trap during drainage, causing odors and potential drainage issues. A box mounted too high can strain the washing machine’s pump, leading to slow drainage, increased pump wear, and potential machine errors. The standard 42-48 inch range provides optimal drainage while preventing these problems.
Can I install a washer box at 50 inches?
Installing a washer box at 50 inches is slightly above the standard recommendation but generally acceptable if it meets local code requirements, which typically allow standpipes up to 96 inches above the trap. At 50 inches, most modern washing machines will drain properly, though you should verify that all connections remain easily accessible at this height and that your specific washing machine’s specifications allow for drain heights in this range.
What happens if my washer box is too low?
If your washer box is installed too low, you may experience several problems including siphoning that drains water from the trap, allowing sewer gases into your home, poor drainage performance during wash cycles, gurgling sounds from the drain, potential for wastewater backup into the machine, and code compliance issues if the installation doesn’t meet minimum height requirements. If you suspect your washer box is too low, have a plumber assess the installation and recommend solutions.
How do I measure the height of my existing washer box?
To measure your existing washer box height, pull your washing machine forward to access the area behind it, then use a tape measure to measure from the finished floor surface directly up to the center of the washer box where the drain connection enters. Compare this measurement to the standard 42-48 inch range to determine if your installation is optimal or may benefit from adjustment.
Do front-load and top-load washers need different box heights?
While both types of washing machines can work within the standard 42-48 inch washer box height range, front-load washers often work best with boxes mounted at 42-44 inches, while top-load machines may be more convenient with boxes at 44-48 inches. The difference relates to the ergonomics of accessing connections relative to each machine type’s design. If using pedestals under front-load washers, you may want to position the box toward the higher end of the range.
Is 60 inches too high for a washer box?
A washer box installed at 60 inches is relatively high but may still function acceptably if it meets code requirements and your washing machine’s specifications allow for this drain height. However, this height may create accessibility challenges when connecting hoses or operating shutoff valves, and you should verify that your machine’s pump can reliably lift water to this height. Most residential installations benefit from staying within the standard 42-48 inch range unless specific circumstances require a higher placement.
Can I adjust the height of an existing washer box?
Adjusting an existing washer box height is possible but involves significant work including opening the wall to access the box and plumbing, disconnecting and removing the existing box, repositioning or extending supply lines and drain connections, installing a new box at the correct height, and repairing and finishing the wall. Due to the complexity and potential for complications, this work is typically best performed by a licensed plumber, especially if permits and inspections are required in your jurisdiction.
Suggested read: The Essential Wash Rack: Everything You Need to Know for Vehicle and Equipment Cleaning
Take Action: Ensuring Proper Washer Box Height in Your Home
Understanding proper washer box height is essential for anyone planning a laundry room installation, renovation, or experiencing problems with an existing setup. Whether you’re a homeowner, contractor, or DIY enthusiast, applying the information in this comprehensive guide will help you create or maintain a laundry plumbing system that operates reliably, meets code requirements, and serves you well for years to come.
If you’re planning a new installation, take time to carefully measure and plan your washer box height before beginning work, ensuring it falls within the recommended 42-48 inch range while accommodating your specific washing machine and household needs. For existing installations experiencing problems, investigating whether improper box height contributes to your issues can help you identify solutions that address root causes rather than just treating symptoms.
Don’t hesitate to consult with licensed plumbing professionals when planning installations or troubleshooting problems. The modest investment in professional expertise or installation pays dividends through proper code compliance, reliable operation, and peace of mind knowing your laundry plumbing system was done right. Your home’s plumbing is too important—and the consequences of mistakes too costly—to take chances with improper washer box height or other installation shortcuts.
For more detailed information about washer box specifications and proper installation heights, visit the International Code Council website, which provides access to the International Plumbing Code and related resources. Taking the time to understand and implement proper washer box height standards ensures your laundry system operates at peak efficiency while protecting your home from potential water damage and code compliance issues.